Computer vision is a rapidly expanding field of study that has revolutionized how machines interpret visual information. It is a subdomain of
artificial intelligence (AI) that enables computers to recognize and understand images and videos like humans do. It involves training computers to extract meaningful information from visual data, such as images, videos, and 3D models. This technology has numerous applications in various industries, including healthcare, automotive, retail, and entertainment, making it an essential aspect of modern society.
History of Computer Vision
The concept of computer vision can be traced back to the 1960s when researchers first began experimenting with computer-based image processing techniques. In 1966, Paul Viola and Michael Jones developed the first face detection algorithm, which began the practical application of computer vision. In the 1970s and 1980s, its algorithms were mainly used for industrial and military purposes, such as analyzing satellite images. However, it was not until the 1990s that computer vision started gaining traction with the development of new algorithms, neural networks, and advancements in computing power.
How Does Computer Vision Work?
Computer vision can be broken down into three main steps: image acquisition, image processing, and image analysis. First, the computer acquires an image or video from a sensor, such as a camera. Next, the image goes through various processing techniques, including filtering, segmentation, and feature extraction. Finally, the extracted features are analyzed and compared with existing datasets to recognize and classify the image.
The success of computer vision heavily depends on the accuracy and robustness of algorithms and the quality of the training data. The algorithms used in this are typically based on machine learning or deep learning methods. These algorithms are trained on large datasets to recognize and classify objects, patterns, and features in images and videos. The more data the algorithm is trained on, the more robust and accurate it becomes at interpreting visual information.

Applications of Computer Vision
It is a rapidly growing field, and its applications are limitless. Here are some of the most common applications of computer vision in various industries:
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry has been one of the early adopters of technology. It is used for various applications in driver-assistance systems like adaptive cruise control and collision avoidance, such as lane detection, object recognition, and pedestrian detection.
Retail
It has revolutionized the retail industry, enabling retailers to provide more personalized shopping experiences to their customers. It is used in inventory management systems to keep track of products, detect out-of-stock items, and prevent theft. In addition, facial recognition technology is used in retail stores for targeted advertising and to identify shoplifters.
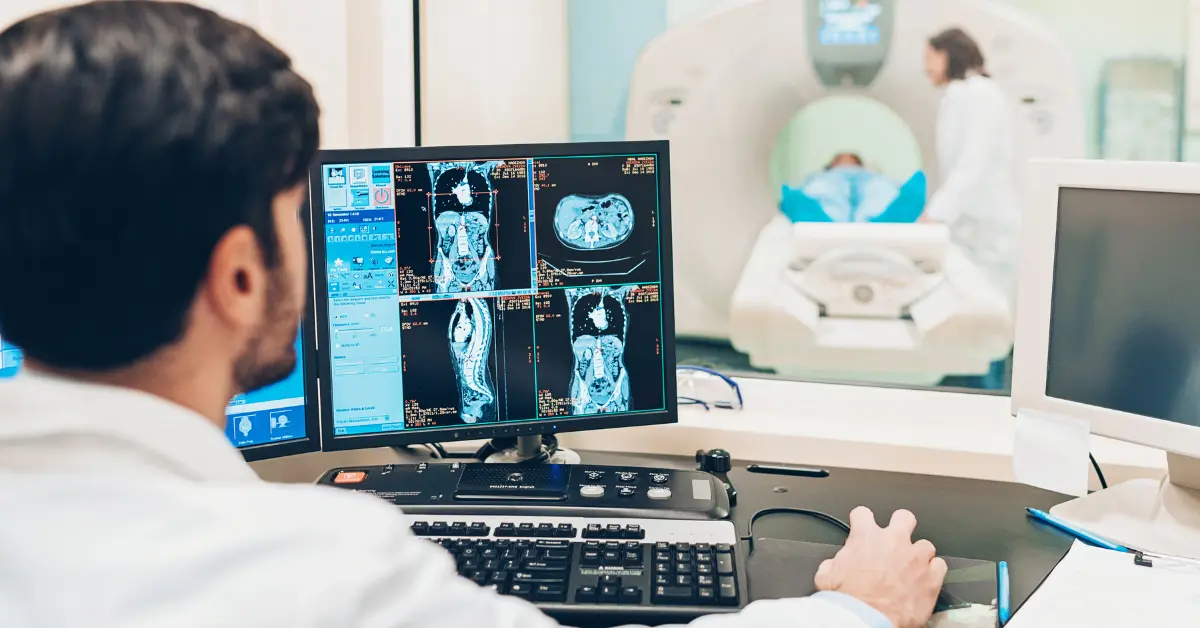
Healthcare
It analyzes medical images such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs in healthcare. It has greatly improved the accuracy and speed of medical diagnoses. Additionally, it is used for remote patient monitoring, detecting diseases early, and assisting in surgeries and medical procedures.
Entertainment
It has also found its way into the entertainment industry. Facial recognition technology is used in video games for interactive experiences, while motion capture technology is used in animated movies to create realistic movements for characters. In addition, it has enhanced the experience of virtual reality and augmented reality applications.
Conclusion
It is a fascinating and rapidly growing field transforming how machines interpret visual information. It has numerous applications in various industries, such as healthcare, automotive, retail, and entertainment, and has greatly improved the efficiency and accuracy of many tasks. As technology advances, we expect to see even more innovative and impactful applications in our daily lives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the difference between computer vision and image processing?
A: Computer vision uses algorithms and machine learning techniques to extract meaningful information from visual data, whereas image processing focuses on manipulating and enhancing images. Image processing is a subset of computer vision; both fields are closely related.
Q: Is computer vision limited to only images and videos?
A: Computer vision can also be applied to 3D models and point clouds. It is used in 3D reconstruction, object tracking, and augmented reality applications.
Q: Can computer vision be used for text recognition?
A: Yes, text recognition, also known as optical character recognition (OCR), is one of the applications of computer vision. It enables computers to recognize and convert text from images or videos into editable text.
Q: What is the future of computer vision?
A: With advancements in AI and computing power, we can expect to see more sophisticated and accurate computer vision applications. This technology is already being explored in areas like autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and security systems. The possibilities are endless, and their potential impact on society has yet to be fully realized.




